Swift學習(6)- 集合型別(程式碼完善版)
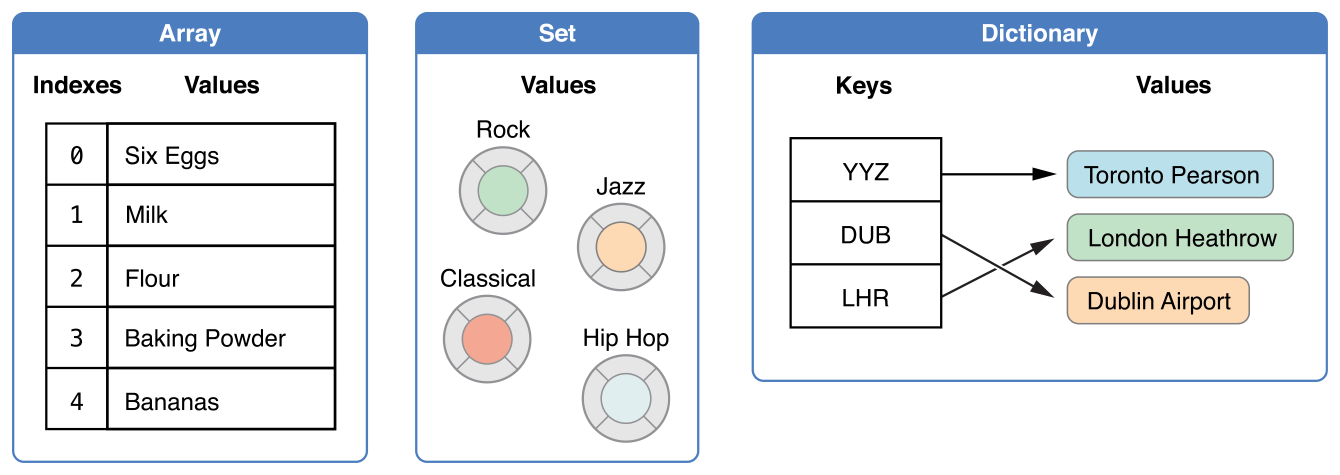
Swift語言提供陣列(Array)、集合(Set)和字典(Dictionary)三種基本的集合型別來儲存集合資料。陣列是有順序的資料集合。集合是無順序且無重複資料的集合。字典是無順序的鍵值對集合。
在Swift中,陣列、集合和字典必須明確指定其所儲存的鍵和值的型別,這樣可以避免插入錯誤型別的值。同理,取得的值也能確保其型別正確。
注意
Swift 的陣列、集合和字典型別皆以泛型集合實作。
集合的可變性
如果將一個陣列、集合或字典指定給變數,該集合將會是可變的。這表示可以在建立後新增、修改或刪除資料項目。如果將陣列、集合或字典指定給常數,則該集合為不可變,其大小與內容皆不可更動。
注意
在不需更動集合時建立不可變集合是良好習慣。這有助於開發者理解程式碼,也能讓
Swift編譯器最佳化集合效能。
陣列(Arrays)
陣列使用有順序的列表來儲存同一型別的多個值。相同的值可以多次出現在陣列的不同位置。
注意
Swift 的
Array型別已橋接至Foundation的NSArray類別。
陣列的簡易語法
在Swift中,陣列的完整寫法為Array<Element>,其中Element是此陣列唯一允許存在的資料型別。也可使用簡化語法[Element]。兩種寫法功能相同,但推薦使用較短的形式,且本文皆以此方式建立陣列。
var initArray: Array<String> = Array<String>()
initArray.append("hello")
print("型別為 Array<String> 的陣列為:\(initArray)")
---
output: 型別為 Array<String> 的陣列為:["hello"]建立空陣列
可使用建構語法建立特定型別的空陣列。
var someInts: [Int] = []
print("someInts 是型別 [Int],有 \(someInts.count) 個項目。") // 印出“someInts 是型別 [Int],有 0 個項目。”
---
output: someInts 是型別 [Int],有 0 個項目。注意,透過建構函式的型別,someInts 的值型別被推斷為 [Int]。
或者,若程式上下文已提供型別資訊,例如函式參數或已定義型別的常數或變數,可用空陣列語法建立空陣列,寫法為 [](一對空方括號):
someInts.append(3)
print("現在的 someInts 是:\(someInts)。")
someInts = []
print("someInts 現在是 \(someInts),但仍是 [Int] 型別。")
---
output: 現在的 someInts 是:[3]。
someInts 現在是 [],但仍是 [Int] 型別。建立具有預設值的陣列
Swift 的 Array 型別也提供可建立特定大小且所有資料皆為預設值的建構方法。可將欲加入新陣列的資料數量(count)及適當型別的初始值(repeating)傳入陣列建構函式。
var threeDoubles = Array(repeating: 0.0, count: 3) // threeDoubles 是 [Double] 陣列,等同於 [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
print("threeDoubles 是 \(threeDoubles)")
---
output: threeDoubles 是 [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]透過兩個陣列相加建立新陣列
可使用加法運算子 + 組合兩個已存在且型別相同的陣列。新陣列的型別會從兩個陣列的型別推斷而來。
var anotherThreeDoubles = Array(repeating: 2.5, count: 3) // anotherThreeDoubles 被推斷為 [Double],等同於 [2.5, 2.5, 2.5]
var sixDoubles = threeDoubles + anotherThreeDoubles // sixDoubles 被推斷為 [Double],等同於 [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 2.5, 2.5, 2.5]
print("sixDoubles 的值為:\(sixDoubles)")
---
output: sixDoubles 的值為:[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 2.5, 2.5, 2.5]以陣列字面量建立陣列
可使用陣列字面量建立陣列,這是一種以一個或多個值建立陣列的簡便方式。陣列字面量是一系列以逗號分隔並由方括號包住的值:
[value 1, value 2, value 3]
以下範例建立一個名為 shoppingList 並儲存 String 的陣列:
var shoppingList: [String] = ["Eggs", "Milk"] // shoppingList 已建立且有兩個初始項目
print("shoppingList 是 \(shoppingList)")
---
output: shoppingList 是 ["Eggs", "Milk"]shoppingList 變數被宣告為「字串型別的陣列」,寫作 [String]。因為此陣列僅允許 String 型別,所以只能存取 String。此處,shoppingList 陣列由兩個 String 值(“Eggs” 與 “Milk”)以陣列字面量建立。
注意
shoppingList 陣列宣告為變數(以 var 建立),而非常數(以 let 建立),因為之後會有更多資料項目加入。
在上述範例中,字面量僅包含兩個 String 值,符合陣列宣告(只能包含 String),因此可將此字面量賦值視為以兩個初始項目建立 shoppingList 的方式。
由於 Swift 的型別推斷機制,當以字面量建立同型別值的陣列時,不必明確指定型別,shoppingList 也可這樣寫:
var shoppingLists = ["Eggs", "Milk"]因所有陣列字面量中的值皆為同型別,Swift 可推斷 [String] 為 shoppingList 的正確型別。
存取與修改陣列
可透過陣列的方法與屬性存取與修改陣列,或使用下標語法。
可使用陣列的唯讀屬性 count 取得陣列中的資料項目數量:
print("The shopping list contains \(shoppingLists.count) items.")
---
output: The shopping list contains 2 items.使用布林屬性 isEmpty 作為檢查 count 是否為 0 的簡便方式:
if shoppingList.isEmpty {
print("The shopping list is empty.")
} else {
print("The shopping list is not empty.")
}
// 印出“The shopping list is not empty.”(shoppingList 不是空的)
---
output: The shopping list is not empty.也可使用 append(_:) 方法在陣列尾端新增資料項目:
shoppingList.append("Flour") // shoppingList 現在有 3 個資料項目,似乎有人要做煎餅
print("加入 'Flour' 後的 shoppingList 值為:\(shoppingList)。")
---
output: 加入 'Flour' 後的 shoppingList 值為:["Eggs", "Milk", "Flour"]。此外,也可使用加法賦值運算子 +=,直接將另一個同型別陣列的資料加到陣列尾端。
shoppingList += ["Baking Powder"] // shoppingList 現在有四項
shoppingList += ["Chocolate Spread", "Chinese", "Butter"] // shoppingList 現在有七項可直接使用下標語法取得陣列中的資料項目,將所需資料項目的索引值放在陣列名稱後的方括號中:
var firstItem = shoppingList[0]
print("shoppingList 的第一項是:\(firstItem)。")
---
output: shoppingList 的第一項是:Eggs。注意
陣列的第一項索引值為 0 而非 1。Swift 陣列索引皆從零開始。
也可用下標語法更改某個有效索引值對應的資料值:
shoppingList[0] = "Six Eggs" // 現在 shoppingList 的第一項是 "Six Eggs" 而非 "Eggs"
print("修改後的 shoppingList 值為:\(shoppingList)")
---
output: 修改後的 shoppingList 值為:["Six Eggs", "Milk", "Flour", "Baking Powder", "Chocolate Spread", "Chinese", "Butter"]使用下標語法時,所用的索引必須有效。例如,嘗試以 shoppingList[shoppingList.count] = "Salt" 在陣列最後新增項目,會產生執行時錯誤。
還可利用下標一次更改一系列資料值,即使新資料與原有資料數量不同。下例將 “Chocolate Spread”、“Chese” 與 “Butter” 替換為 “Bananas” 與 “Apples”。
shoppingList[4...6] = ["Bananas", "Apples"] // shoppingList 現在有 6 項
print("shoppingList 現在是:\(shoppingList)")
// 透過呼叫陣列的 `insert(_:at:)` 方法,在指定索引前插入資料項目:
shoppingList.insert("Maple Syrup", at: 0) // shoppingList 現在有 7 項
// 現在列表的第一項是 "Maple Syrup"
print("shoppingList 現在的第一項是:\(shoppingList[0])")
// 此次 `insert(_:at:)` 方法呼叫,將值為 "Maple Syrup" 的新資料項目插入列表最前面,並以 0 為索引。
---
output: shoppingList 現在是:["Six Eggs", "Milk", "Flour", "Baking Powder", "Bananas", "Apples"]
shoppingList 現在的第一項是:Maple Syrup同樣可使用 remove(at:) 方法移除陣列的某一項。此方法會將陣列中特定索引的資料項目移除並回傳被移除的資料(若不需可忽略)。
let mapleSyrup = shoppingList.remove(at: 0) // 現在 shoppingList 只剩 6 項,不含 "Maple Syrup",常數 mapleSyrup 等於 "Maple Syrup"
print("mapleSyrup 的值等於:\(mapleSyrup),shoppingList 等於:\(shoppingList).")
---
output: mapleSyrup 的值等於:Maple Syrup,shoppingList 等於:["Six Eggs", "Milk", "Flour", "Baking Powder", "Bananas", "Apples"].注意
若嘗試以超出範圍的索引存取或修改資料,會引發執行時錯誤。可在使用索引前,將索引值與陣列的
count屬性比較以檢查其有效性。除非count為 0(表示為空陣列),最大索引值為count - 1,因陣列索引從零開始。
資料項目被移除後,陣列中的空缺會自動補齊,因此現在索引值為 0 的資料項目值又變成 “Six eggs”。
firstItem = shoppingList[0] // firstItem 現在等於 "Six Eggs"
print("此時 shoppingList 首位是:\(firstItem)")
// 若只想移除陣列最後一項,可用 `removeLast()` 方法而非 `remove(at:)`,可避免需取得陣列的 `count` 屬性。與後者一樣,前者也會回傳被移除的資料項目。
let apples = shoppingList.removeLast() // 陣列最後一項被移除,shoppingList 現在只剩 5 項,不含 "Apples",常數 apples 現在等於 "Apples"
print("常數 apples 現在的值:\(apples),shoppingList 等於:\(shoppingList).")
// 同樣還有 `removeFirst()` 方法,直接移除陣列第一項。
let sixEggs = shoppingList.removeFirst()
---
output: 此時 shoppingList 首位是:Six Eggs
常數 apples 現在的值:Apples,shoppingList 等於:["Six Eggs", "Milk", "Flour", "Baking Powder", "Bananas"].陣列的遍歷
可使用 for-in 迴圈遍歷陣列中所有資料項目:
for item in shoppingList {
print(item) // Six eggs; Milk; Flour; Baking Powder; Bananas
}
---
output: Milk
Flour
Baking Powder
Bananas若同時需取得每個資料項的值與索引,可用 enumerated() 方法遍歷陣列。enumerated() 會回傳由索引值與資料值組成的元組。索引值從零開始,每次加一;若枚舉整個陣列,索引值會與資料值一一對應。可將此元組分解為臨時常數或變數進行遍歷:
for (index, value) in shoppingList.enumerated() {
print("Item \(String(index + 1)): \(value)") // Item 1: Milk; Item 2: Flour; Item 3: Baking Powder; Item 4: Bananas
}
---
output: Item 1: Milk
Item 2: Flour
Item 3: Baking Powder
Item 4: Bananas集合(Sets)
集合用來儲存同一型別但無特定順序的值。當集合元素順序不重要,或希望確保每個元素僅出現一次時,可用集合取代陣列。
注意
Swift 的 Set 型別已橋接至 Foundation 的 NSSet 類別。
集合型別的雜湊值
一個型別若要儲存在集合中,必須可雜湊(Hashable),也就是必須提供計算其雜湊值的方法。雜湊值為 Int 型別,相等的物件雜湊值必須相同,例如 a == b,則必須 a.hashValue == b.hashValue。
Swift 的所有基本型別(如 String、Int、Double 和 Bool)預設皆可雜湊,可作為集合值型別或字典鍵型別。無關聯值的列舉成員值預設也可雜湊。
注意
可使用自訂型別作為集合值型別或字典鍵型別,但需讓自訂型別遵循 Swift 標準函式庫的 Hashable 協定。遵循 Hashable 協定的型別需提供型別為 Int 的唯讀屬性 hashValue。由型別的 hashValue 屬性回傳的值,不需在同一程式的不同執行週期或不同程式間保持一致。
因 Hashable 遵循 Equatable 協定,故遵循該協定的型別也必須實作「是否相等」運算子(==)。Equatable 協定要求任何遵循 == 的實例間皆為一種等價關係。亦即,對於 a、b、c 三個值,== 的實作必須滿足下列三種情況:
- a == a(自反性)
- a == b 意味著 b == a(對稱性)
- a == b && b == c 意味著 a == c(傳遞性)
集合型別語法
Swift 中的集合型別寫作 Set<Element>,其中 Element 表示集合中允許儲存的型別。與陣列不同,集合無等價的簡化形式。
建立與建構空集合
可透過建構器語法建立特定型別的空集合
var letters = Set<Character>()
print("Letters 是型別 Set<Character>,有 \(letters.count) 個項目。") // 印出“Letters 是型別 Set<Character>,有 0 個項目。”
---
output: Letters 是型別 Set<Character>,有 0 個項目。注意
透過建構器,此處 letters 變數型別被推斷為 Set
。
此外,若上下文已提供型別資訊,如作為函式參數或已知型別的變數或常數,可用空陣列字面量建立空集合。
letters.insert("A") // letters 現在含有 1 個 Character 型別的值
print("現在 Letters 值為:\(letters)")
letters = [] // letters 現在是空 Set,但仍為 Set<Character> 型別
print("此時 Letters 值為:\(letters)")
---
output: 現在 Letters 值為:["A"]
此時 Letters 值為:[]以陣列字面量建立集合
可用陣列字面量建立集合,相當於簡化方式將一個或多個值作為集合元素。
下例建立一個名為 favoriteGenres 的集合來儲存 String 型別的值。
var favoriteGenres: Set<String> = ["Rock", "Classical", "Hip hop"] // favoriteGenres 建構為含三個初始值的集合此 favoriteGenres 變數宣告為「String 型別的集合」,寫作 Set<String>。由於此集合指定值為 String 型別,僅能儲存 String。此處 favoriteGenres 變數有三個 String 型別初始值(“Rock”、“Classical”、“Hip hop”),以陣列字面量寫成。
注意
favoriteGenres 宣告為變數(以 var 標示),而非常數(以 let 標示),因之後會有元素新增或移除。
集合型別無法直接從陣列字面量推斷型別,因此必須明確宣告 Set 型別。不過,因 Swift 的型別推斷功能,若以陣列字面量建立集合且所有元素型別相同,則無需寫出集合具體型別。FavoriteGenres 的建構可簡化如下:
var FavoriteGenres: Set = ["Rock", "Classical", "Hip hop"]因所有陣列字面量元素型別皆為 String,Swift 可推斷 Set<String> 為 favoriteGenres 變數的正確型別。
存取與修改集合
可透過集合的屬性與方法存取與修改集合
為取得集合中元素數量,可用其唯讀屬性 count:
print("I have \(FavoriteGenres.count) favorite music genres.") // 印出“I have 3 favorite music genres.”
---
output: I have 3 favorite music genres.使用布林屬性 isEmpty 作為檢查 count 是否為 0 的簡便方式:
if FavoriteGenres.isEmpty {
print("As far as music goes, I'm not picky.")
} else {
print("I have particular music preferences.")
} // 印出“I have particular music preferences.”
---
output: I have particular music preferences.可呼叫集合的 insert(_:) 方法新增新元素:
FavoriteGenres.insert("Jazz") // FavoriteGenres 現在包含 4 個元素。
print("FavoriteGenres 現在包含 \(FavoriteGenres.count) 個元素,其值為:\(FavoriteGenres)")
---
output: FavoriteGenres 現在包含 4 個元素,其值為:["Classical", "Jazz", "Hip hop", "Rock"]可呼叫集合的 remove(_:) 方法刪除元素,若該元素存在則刪除並回傳其值,若集合不含該值則回傳 nil。此外,集合可用 removeAll() 方法刪除所有元素。
if let removeGenre = FavoriteGenres.remove("Rock") {
print("\(removeGenre)? I'm over it!")
} else {
print("I never much cared of that!")
} // 印出“Rock? I'm over it!”
---
output: Rock? I'm over it!使用 contains(_:) 方法檢查集合中是否包含特定值:
if FavoriteGenres.contains("Funk") {
print("I get up on the good foot.")
} else {
print("It's too funky in here.")
} // 印出"It's too funky in here."
---
output: It's too funky in here.遍歷集合
可在 for-in 迴圈中遍歷集合所有值。
for genre in FavoriteGenres {
print("\(genre)")
} // Hip hop; // Classical; // Jazz 無順序排列
---
output: Classical
Jazz
Hip hopSwift 的 Set 型別無特定順序,若要依特定順序遍歷集合中的值,可用 sorted() 方法,回傳有序陣列,元素順序由 < 運算子比較決定。
for genre in FavoriteGenres.sorted() {
print("\(genre)")
} // Classical; // Hip hop; // Jazz 有順序排列
---
output: Classical
Hip hop
Jazz集合操作
可高效完成集合的基本操作,如將兩個集合合併、判斷兩集合的共同元素,或判斷兩集合是否全包含、部分包含或不相交。
基本集合操作
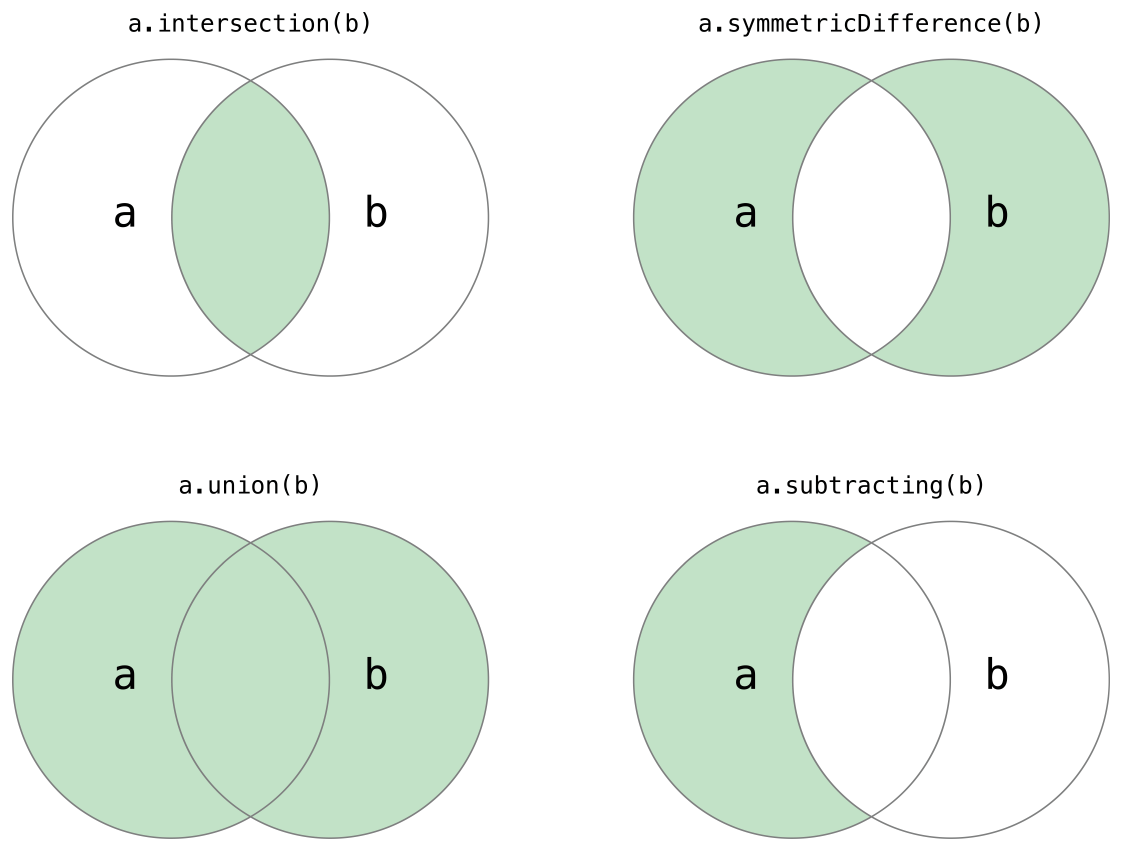
- 使用
intersection(_:)方法依兩集合交集建立新集合。 - 使用
symmetricDifference(_:)方法依兩集合不相交的值建立新集合。 - 使用
union(_:)方法依兩集合所有值建立新集合。 - 使用
subtracting(_:)方法依不在另一集合中的值建立新集合。
let oddDigits: Set = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
let evenDigits: Set = [0, 2, 4, 6, 8]
let singleDigitPrimeNumbers: Set = [2, 3, 5, 7]
print("Union: \(oddDigits.union(evenDigits).sorted())") // [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
print("InterSection: \(oddDigits.intersection(evenDigits).sorted())") // []
print("SubTracting: \(oddDigits.subtracting(singleDigitPrimeNumbers).sorted())") // [1, 9]
print("SymmetricDifference: \(oddDigits.symmetricDifference(singleDigitPrimeNumbers).sorted())") // [1, 2, 9]
---
output: Union: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
InterSection: []
SubTracting: [1, 9]
SymmetricDifference: [1, 2, 9]集合成員關係與相等
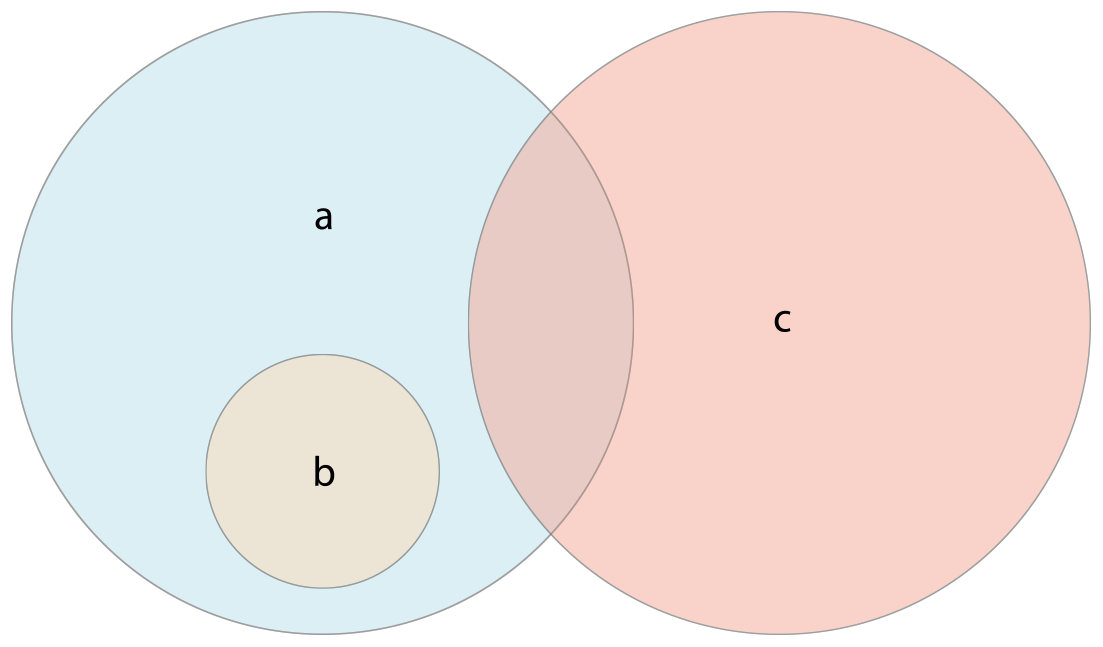
- 使用「是否相等」運算子
==判斷兩集合所含值是否相同。 - 使用
isSubset(of:)方法判斷一集合所有值是否也包含於另一集合。 - 使用
isSuperset(of:)方法判斷一集合是否包含另一集合所有值。 - 使用
isStrictSubset(of:)或isStrictSuperset(of:)方法判斷一集合是否為另一集合的真子集合或真父集合且兩集合不相等。 - 使用
isDisjoint(with:)方法判斷兩集合是否無共同值(是否無交集)。
let houseAnimals: Set = ["🐶", "🐱"]
let farmAnimals: Set = ["🐮", "🐔", "🐑", "🐶", "🐱"]
let cityAnimals: Set = ["🐦", "🐭"]
print("IsSubset? \(houseAnimals.isSubset(of: farmAnimals))") // 印出 "IsSubset? true"
print("IsSuperset? \(farmAnimals.isSuperset(of: houseAnimals))") // 印出 "IsSuperset? true"
print("IsDisjoint? \(farmAnimals.isDisjoint(with: cityAnimals))") // 印出 "IsDisjoint? true"
---
output: IsSubset? true
IsSuperset? true
IsDisjoint? true字典
字典是一種無順序的集合,儲存鍵值對關係,所有鍵需為同型別,所有值也需為同型別。每個值(value)皆關聯唯一鍵(key),鍵作為字典中該值的識別。與陣列不同,字典中的資料項目無特定順序。當需透過識別(鍵)存取資料時使用字典,這與現實中查字典的方式相似。
注意
Swift 的 Dictionary 型別已橋接至 Foundation 的 NSDictionary 類別。
字典型別簡化語法
Swift 的字典以 Dictionary<Key, Value> 定義,其中 Key 為可作為鍵的型別,Value 為對應於這些鍵所儲存值的型別。
注意
字典的 Key 型別必須遵循 Hashable 協定,與 Set 的值型別相同。
也可用 [Key: Value] 這種簡化形式表示字典型別。兩種寫法功能相同,但推薦後者,且本文皆以此方式表示字典型別。
建立空字典
可如同陣列般,使用建構語法建立特定型別的空字典:
var namesOfInteger: Dictionary<Int, String> = Dictionary<Int, String>() // 使用 Dictionary<Key, Value> 定義字典
print("使用 Dictionary<Key, Value> 定義字典:\(namesOfInteger)")
var namesOfIntegers: [Int: String] = [:] // 簡化語法,首選!
print("簡化語法,首選:\(namesOfIntegers)")
---
output: 使用 Dictionary<Key, Value> 定義字典:[:]
簡化語法,首選:[:]此範例建立一個 [Int: String] 型別的空字典來儲存整數的英文名稱。其鍵為 Int,值為 String。
若上下文已提供型別資訊,可用空字典字面量建立空字典,寫作 [:](一對方括號中放冒號):
namesOfIntegers[16] = "sixteen" // namesOfIntegers 現在包含一個鍵值對
namesOfIntegers = [:] // namesOfIntegers 又成為 [Int: String] 型別的空字典以字典字面量建立字典
可用字典字面量建立字典,語法與前述陣列字面量類似。字典字面量是一種將一或多個鍵值對寫作 Dictionary 集合的快捷方式。
一個鍵值對為鍵與值的組合,在字典字面量中,每個鍵值對的鍵和值以冒號分隔。這些鍵值對構成一個列表,彼此以逗號分隔,並整體包在一對方括號中:
// [key 1: value 1, key 2: value 2, key 3: value 3]下例建立一個儲存國際機場名稱的字典。此字典的鍵為三個字母的國際航空運輸協會代碼,值為機場名稱:
var airposts: [String: String] = ["HFE": "Hefei Xinqiao", "NKG": "Nanjing Lukou", "PKX":"Beijing Daxing", "SHA":"Shanghao Hongqiao"]
print("China Main Airpots: \(airposts)")
---
output: China Main Airpots: ["HFE": "Hefei Xinqiao", "NKG": "Nanjing Lukou", "PKX": "Beijing Daxing", "SHA": "Shanghao Hongqiao"]airports 字典宣告為 [String: String] 型別,表示此字典的鍵和值皆為 String 型別。
注意
airports 字典宣告為變數(以 var 建立),而非常數(以 let 建立),因後續會有更多機場加入此字典。
airports 字典以字典字面量初始化,包含四個鍵值對。其型別符合 airports 變數宣告(僅允許 String 鍵與 String 值),因此此字典字面量賦值即為以四個初始資料項目建立 airports 字典。
如同陣列,若以字典字面量建立字典時,其鍵和值皆為一致型別,則無需明確指定型別,airports 字典亦可簡寫如下:
var chinaAirports = ["HFE": "Hefei Luogang", "NKG": "Nanjing Lukou", "PKX":"Beijing Daxing", "SHA":"Shanghao Hongqiao"]因此語句中所有鍵值皆為同型別,Swift 可推斷 [String: String] 為 airports 字典的正確型別。
存取與修改字典
可透過字典的方法與屬性存取與修改字典,或使用下標語法。
如同陣列,可用 Dictionary 的唯讀屬性 count 取得字典的資料項目數量:
print("The dictionary of chinaAirports contains \(chinaAirports.count) items.") // 印出"The dictionary of chinaAirports contains 4 items."
---
output: The dictionary of chinaAirports contains 4 items.使用布林屬性 isEmpty 作為檢查 count 是否為 0 的簡便方式:
if chinaAirports.isEmpty {
print("The chinaAirports dictionary is empty.")
} else {
print("The chinaAirports dictionary is not empty.")
} // 印出"The chinaAirports dictionary is not empty."
---
output: The chinaAirports dictionary is not empty.可用下標語法為字典新增新資料項目,使用適當型別的鍵作為下標索引,並指定適當型別的新值:
airposts["XIY"] = "Xi'an" // airports 字典現在有五個資料項目
print(airposts)
---
output: ["HFE": "Hefei Xinqiao", "NKG": "Nanjing Lukou", "PKX": "Beijing Daxing", "XIY": "Xi\'an", "SHA": "Shanghao Hongqiao"]也可用下標語法更改特定鍵對應的值:
airposts["XIY"] = "Xi'an Xianyang" // "XIY" 對應的值被修改為 "Xi'an Xianyang"
print(airposts)
---
output: ["HFE": "Hefei Xinqiao", "NKG": "Nanjing Lukou", "PKX": "Beijing Daxing", "XIY": "Xi\'an Xianyang", "SHA": "Shanghao Hongqiao"]作為下標語法的替代方式,字典的 updateValue(_:forKey:) 方法可設定或更新特定鍵對應的值。如同上述下標範例,updateValue(_:forKey:) 方法在鍵不存在時會設定新值,存在時則更新既有值。與下標方式不同,updateValue(_:forKey:) 方法會回傳更新前的原值。如此可檢查更新是否成功。
updateValue(_:forKey:) 方法會回傳對應值型別的可選型別。例如:對於儲存 String 值的字典,此函式會回傳 String? 或可選 String 型別的值。若更新前有值,則此可選值包含舊值,否則為 nil:
if let oldValue = airposts.updateValue("Hefei Xinqiao", forKey: "HFE") {
print("The old value for HFE was \(oldValue).")
} // 印出"The old value for HFE was Hefei Xinqiao."
---
output: The old value for HFE was Hefei Xinqiao.也可用下標語法自字典檢索特定鍵對應的值。因請求的鍵可能無對應值,字典的下標存取會回傳對應值的可選型別。若字典包含請求鍵對應的值,下標會回傳包含該值的可選型別,否則回傳 nil:
if let airportName = airposts["HFE"] {
print("The name of the airport is \(airportName).")
} else {
print("That airport is not in the airports dictionary.")
} // 印出"The name of the airport is Hefei Xinqiao."
---
output: The name of the airport is Hefei Xinqiao.還可用下標語法,將某鍵對應值設為 nil,以自字典移除鍵值對:
airposts["CAN"] = "Guangzhou Baoan" // Baoan 機場在深圳,因此刪除它
print(airposts)
airposts["CAN"] = nil // CAN 現在被移除
print(airposts)
---
output: ["HFE": "Hefei Xinqiao", "NKG": "Nanjing Lukou", "PKX": "Beijing Daxing", "XIY": "Xi\'an Xianyang", "CAN": "Guangzhou Baoan", "SHA": "Shanghao Hongqiao"]
["HFE": "Hefei Xinqiao", "NKG": "Nanjing Lukou", "PKX": "Beijing Daxing", "XIY": "Xi\'an Xianyang", "SHA": "Shanghao Hongqiao"]此外,removeValue(forKey:) 方法也可用來自字典移除鍵值對。此方法在鍵值對存在時會移除該鍵值對並回傳被移除的值,否則回傳 nil:
if let removeValue = airposts.removeValue(forKey: "NKG") {
print("The removed airport's name is \(removeValue).")
} else {
print("The airports dictionary does not contain a value for NKG.")
} // 印出"The removed airport's name is Nanjing Lukou."
---
output: The removed airport's name is Nanjing Lukou.字典遍歷
可用 for-in 迴圈遍歷字典中的鍵值對。每個字典資料項目皆以 (Key, Value) 元組回傳,可用臨時常數或變數分解這些元組。
for (airportCode, airportName) in airposts {
print("\(airportCode): \(airportName)")
} // HFE: Hefei Xinqiao; // PKX: Beijing Daxing; //SHA: Shanghao Hongqiao; // XIY: Xi'an Xianyang
---
output: HFE: Hefei Xinqiao
PKX: Beijing Daxing
XIY: Xi'an Xianyang
SHA: Shanghao Hongqiao透過存取 keys 或 values 屬性,可遍歷字典的鍵或值:
for airportCode in airposts.keys {
print("Airport code: \(airportCode)")
}
for airportName in airposts.values {
print("Airport name: \(airportName)")
}
---
output: Airport code: HFE
Airport code: PKX
Airport code: XIY
Airport code: SHA
Airport name: Hefei Xinqiao
Airport name: Beijing Daxing
Airport name: Xi'an Xianyang
Airport name: Shanghao Hongqiao若需將字典的鍵集合或值集合作為接受 Array 實例的 API 參數,可直接用 keys 或 values 屬性建立新陣列。
let airportCodes = [String](airposts.keys) // airportCodes 為 ["HFE", "PKX", "SHA", "XIY"]
print(airportCodes)
let airportNames = [String](airposts.values) // airportNames 為 ["Hefei Xinqiao", "Beijing Daxing", "Shanghai Hongqiao", "Xi'an Xianyang"]
print(airportNames)
---
output: ["HFE", "PKX", "XIY", "SHA"]
["Hefei Xinqiao", "Beijing Daxing", "Xi\'an Xianyang", "Shanghao Hongqiao"]Swift 的 Dictionary 為無順序集合型別。若要以特定順序遍歷字典的鍵或值,可對字典的 keys 或 values 屬性使用 sorted() 方法。