Swift學習(5)- 字串與字元(程式碼完善版)
字串是一系列字元的集合,例如「Hello, world」、「albatross」。Swift 的字串以 String 型別來表示。String 的內容可以用多種方式存取,例如作為 Character 值的集合。
Swift 的 String 與 Character 型別提供了一種快速且相容 Unicode 的方式來處理程式中的文字內容。建立與操作字串的語法與 C 語言中的字串操作類似,簡潔且易讀。只要用 + 符號就能輕鬆將兩個字串串接起來。和 Swift 其他值一樣,字串是否可變取決於它被定義為常數還是變數。
開發者可以在既有字串中插入常數、變數、字面量與運算式,形成更長的字串,這個過程稱為字串插值。特別是在顯示、儲存或列印自訂字串值時,字串插值特別有用。
雖然語法簡單,Swift 中的 String 型別實作卻非常快速且現代化。每個字串都是由與編碼無關的 Unicode 字元組成,並支援多種 Unicode 表現形式來存取字元。
注意
Swift 的 String 型別與 Foundation 的 NSString 類別無縫橋接。Foundation 也擴充了 String,使其可以存取 NSString 型別中定義的方法。這代表呼叫那些 NSString 的方法時不需要進行型別轉換。
字串字面量
開發者可以在程式碼中使用預先定義的字串值作為字串字面量。字串字面量是由一對雙引號包住、具有固定順序的字元集合。
字串字面量可用來為常數與變數提供初始值。
let someString = "Some string literal value" // 字串字面量初始化 String 型別常數注意,Swift 會推斷 someString 常數為字串型別,是因為它用字面量方式初始化。
多行字串字面量
如果需要一個跨越多行的字串,可以使用多行字串字面量:由一對三個雙引號包住的文字字元集合。
let quotation = """
The White Rabbit put on his spectacles. "Where shall I begin, please your Majesty?" he asked.
"Begin at the beginning" the King said gravely, "and go on til you come to the end; then stop."
"""
print(quotation)
---
output: The White Rabbit put on his spectacles. "Where shall I begin, please your Majesty?" he asked.
"Begin at the beginning" the King said gravely, "and go on til you come to the end; then stop."多行字串字面量包含所有在開啟與關閉引號 """ 之間的行。字串從開啟引號 """ 之後的第一行開始,到關閉引號 """ 之前為止。這代表開頭或結尾的引號旁沒有換行符號。
下例中兩個字串其實一樣,雖然第二個用了多行字串的形式。
let singleLineString = "These are the same."
let multiLineString = """
These are the same.
"""
print("單行字串:\(singleLineString)")
print("多行字串:\(multiLineString)")
---
output: 單行字串:These are the same.
多行字串:These are the same.如果多行字串字面量中包含換行符,則字串中也會包含換行符。如果想為了程式碼可讀性換行,但又不想在字串中出現換行符,可以在行尾加上反斜線 \ 作為續行符。
let softWrappedQuotation = """
The White Rabbit put on his spectacles. "Where shall I begin, \
please your Majesty?" he asked.
"Begin at the beginning," the King said gravely, "and go on \
till you come to the end; then stop."
"""
print("使用了換行符的 quotation:\(softWrappedQuotation)")
---
output: 使用了換行符的 quotation:The White Rabbit put on his spectacles. "Where shall I begin, please your Majesty?" he asked.
"Begin at the beginning," the King said gravely, "and go on till you come to the end; then stop."若要讓多行字串字面量以換行符開始與結束,請將換行寫在第一行與最後一行,例如:
let lineBreaks = """
This string starts with a line break.
It also ends with a line break.
"""
print(lineBreaks)
---
output:
This string starts with a line break.
It also ends with a line break.多行字串字面量可以縮排以符合周圍程式碼。關閉引號 """ 前的空白字元會告訴 Swift 編譯器其他各行要忽略多少空白字元。不過,如果某行前面的空白字元超過關閉引號前的空白字元,超出部分會被包含在多行字串字面量中。
let linesWithIndentation = """
This line doesn't begin with whitespace.
This line begins with four spaces.
This line doesn't begin with whitespace.
""" // 關閉引號前的空白有 4 個空格
print(linesWithIndentation)
---
output: This line doesn't begin with whitespace.
This line begins with four spaces.
This line doesn't begin with whitespace.上例中,雖然整個多行字串字面量都有縮排(原始碼縮排),第一行與最後一行沒有以空白字元開始(實際變數值)。中間那行的縮排比關閉引號前的空白還多,所以行首有 4 個空格。
字串字面量的特殊字元
字串字面量可以包含以下特殊字元:
- 跳脫字元:
\0(空字元)、\\(反斜線)、\t(定位字元)、\n(換行)、\r(回車)、\"(雙引號)、\'(單引號) Unicode標量,寫成\u{n}(u 小寫),其中n為 1~8 位十六進位數且為有效的Unicode位置碼
以下程式碼示範各種特殊字元的用法。
let wiseWords = "\"Imagination is more important than knowledge.\" - Einstein"
let dollarSign = "\u{24}" // $,Unicode 標量 U+0024
let blackHeart = "\u{2665}" // ♥,Unicode 標量 U+2665
let sparklingHeart = "\u{1F496}" // 💖,Unicode 標量 U+1F496
print(wiseWords)
print(dollarSign, terminator: " ")
print(blackHeart, terminator: " ")
print(sparklingHeart)
---
output: "Imagination is more important than knowledge." - Einstein
$ ♥ 💖由於多行字串字面量用三個雙引號而不是一個,所以可以直接在多行字串字面量中使用雙引號 " 而不用跳脫字元 \。若要在多行字串字面量中使用 """,就必須用至少一個跳脫字元(可用 """ 跳脫三個雙引號)。
let threeDoubleQuotes = """
Escaping the first quote \"""
Escaping all three quotes \"\"\"
"""
print(threeDoubleQuotes)
---
output: Escaping the first quote """
Escaping all three quotes """擴充字串分隔符
可以將字串字面量放在擴充分隔符中,這樣字串中的特殊字元會被直接包含而不會被跳脫。將字串放在雙引號 " 中,並用井字號 # 包起來。例如,列印字串字面量 #"Line 1 \n Line2"# 會直接顯示 \n 而不是換行。
如果需要字串字面量中的特殊效果,請在跳脫字元 \ 後面加上與起始位置相同數量的 #。例如,若字串是 #"Line 1 \nLine 2"# 並想要換行效果,可以用 #"Line 1 \#nLine 2"#。同理,###"Line 1 \###nLine 2"### 也可以。
擴充分隔符建立的字串字面量也可以是多行字串字面量。可以用擴充分隔符在多行字串中包含 """,覆蓋原本的結束字串預設行為。例如:
let threeMoreDoubleQuotationMarks = #"""
Here are three more double quotes: """
Good! Good!
"""#
print(threeMoreDoubleQuotationMarks)
---
output: Here are three more double quotes: """
Good! Good!初始化空字串
要建立一個空字串作為初始值,可以將空字串字面量指派給變數,或初始化一個新的 String 實例。
var emptyString = "" // 空字串字面量
var anotherEmptyString = String() // 初始化方法
// 兩個字串皆為空且等價可以透過檢查 Bool 型別的 isEmpty 屬性來判斷字串是否為空。
if emptyString.isEmpty {
print("Nothing to see here.") // 輸出「Nothing to see here.」
}
---
output: Nothing to see here.字串可變性
可以將特定字串指派給變數來修改它,或指派給常數來保證它不會被修改。
var variableString = "Horse"
variableString += " and carriage" // variableString 現在為「Horse and carriage」
print(variableString)
let constantString = "Highlander"
//constantString += " and another Hignlander" // 若取消這行註解,編譯器會報錯:Left side of mutating operator isn't mutable: 'constantString' is a 'let' constant
print(constantString)
---
output: Horse and carriage
Highlander注意
在 Objective-C 與 Cocoa 中,需要選擇兩個不同的類別(NSString 與 NSMutableString)來指定字串是否可變。
字串是值型別
在 Swift 中,String 型別是值型別。如果開發者建立一個新的字串,當它進行常數、變數指派,或在函式/方法中傳遞時,會進行值複製。在上述任何情況下,都是對既有字串值建立新副本,並對該副本而非原始字串進行傳遞或指派。
Swift 預設的複製行為保證了函式/方法傳遞的字串所有權屬於自己,不論該值來自哪裡,都可以確信原始字串不會被修改,除非開發者自己去改。
在實際編譯時,Swift 編譯器會最佳化字串的使用,使實際的複製只發生在絕對必要時,這代表將字串作為值型別同時也能有極高效能。
使用字元
可以用 for-in 迴圈遍歷字串,取得字串中每個字元的值。
for character in "Dog!🐶" {
print(character)
}
// 另外,也可以明確標註為 `Character` 型別並用字元字面量指派,建立獨立的字元常數或變數。
let exclamationMark: Character = "!"
// 字串也可以傳入一個值型別為 `Character` 的陣列來初始化。
let catCharacters: [Character] = ["c", "a", "t", "!", "🐱"]
let catString = String(catCharacters)
print(catString) // 輸出 "cat!🐱"
---
output: D
o
g
!
🐶
cat!🐱串接字串與字元
字串可以用加法運算子 + 串接在一起(或稱「連接」)建立新字串。
let string1 = "hello"
let string2 = " jensen"
var welcome = string1 + string2 // welcome 現在等於「hello jensen」
print(welcome)
---
output: hello jensen當然也可以用加法指派運算子 += 將字串加到已存在的字串變數上。
var instruction = "look over"
instruction += string2 // instruction 現在等於「look over jensen」
print(instruction)
---
output: look over jensen可以用 append() 方法將字元加到字串變數的尾端。
let questionMark: Character = "?"
welcome.append(questionMark) // welcome 現在等於「hello jensen?」
print(welcome)
---
output: hello jensen?注意
不能將字串或字元加到已存在的字元變數上,因為字元變數只能包含一個字元。
如果需要用多行字串字面量來串接字串,且需要每一行都以換行符結尾(包含最後一行)。
let badStart = """
one
two
"""
let end = """
three
"""
print(badStart + end) // 輸出兩行:one\ntwothree
let goodStart = """
one
two
"""
print(goodStart + end) // 輸出三行:one\ntwo\nthree
---
output: one
twothree
one
two
three上例中,把 badStart 和 end 串接起來的字串不是我們想要的結果,因為 badStart 最後一行沒有換行符,會和 end 的第一行合併。相反地,goodStart 每行都以換行符結尾,所以和 end 串接的字串總共有三行。
字串插值
字串插值是一種建立新字串的方式,可以在其中包含常數、變數、字面量與運算式。字串字面量與多行字串字面量都可以用字串插值,插入的內容以反斜線加括號 \() 包住。
let multiplier = 3
let message = "\(multiplier) times 2.5 is \(Double(multiplier) * 2.5)" // message 是「3 times 2.5 is 7.5」
print(message)
---
output: 3 times 2.5 is 7.5上例中,multiplier 以 \(multiplier) 插入到字串字面量中。建立字串時會計算插值,並將該佔位符替換為 multiplier 的實際值。
multiplier 的值也作為字串中後面運算式的一部分。該運算式計算 Double(multiplier) * 2.5 的值並將結果(7.5)插入字串。這裡運算式寫成 \(Double(multiplier) * 2.5) 並包在字串字面量中。
可以用擴充字串分隔符建立字串,來包含不想被當作字串插值處理的字元。
print(#"Write an interpolated string in Swift using \(multiplier)."#) // 輸出「Write an interpolated string in Swift using \(multiplier).」
---
output: Write an interpolated string in Swift using \(multiplier).如果要在用擴充字串分隔符的字串中使用字串插值,需要在反斜線後加上與開頭和結尾相同數量的擴充分隔符。
print(#"6 times 7 is \#(6 * 7)"#) // 輸出「6 times 7 is 42」
---
output: 6 times 7 is 42注意
插值字串中括號內的運算式不能包含未跳脫的反斜線
\,也不能包含回車或換行。不過,插值字串可以包含其他字面量。
Unicode
Unicode 是一個用於在不同書寫系統中對文字進行編碼、表示與處理的國際標準。它讓開發者能用標準格式表示來自任何語言的幾乎所有字元,並能對文字檔或網頁等外部資源中的字元進行讀寫。Swift 的 String 與 Character 型別完全相容 Unicode 標準。
Unicode 標量
Swift 的 String 型別是基於 Unicode 標量建立的。Unicode 標量是對應字元或修飾符的唯一 21 位數字,例如 U+0061 表示小寫拉丁字母(LATIN SMALL LETTER A)(「a」),U+1F425 表示小雞表情(FRONT-FACING BABY CHICK)(「🐤」)。(UTF-32 編碼最大長度為 4 位元組,四位元組模板:11110XXX 10XXXXXX 10XXXXXX 10XXXXXX,因此有 21 位數字)
請注意,並非所有 21 位 Unicode 標量值都分配給字元,有些標量保留給未來分配或用於 UTF-16 編碼。已分配的標量值通常也有名稱,例如上例的 LATIN SMALL LETTER A 與 FRONT-FACING BABY CHICK。
可擴充字形群集
每個 Swift 的 Character 型別代表一個可擴充字形群集。可擴充字形群集構成人類可讀的單一字元,由一個或多個(組合時)Unicode 標量序列組成。
舉例來說,字母 é 可以用單一的 Unicode 標量 é(LATIN SMALL LETTER E WITH ACUTE,U+00E9)表示。也可以用標準字母 e(LATIN SMALL LETTER E,U+0065)加上一個急性重音(COMBINING ACUTE ACCENT,U+0301)標量,這樣一對標量也能表示同樣的字母 é。這個急性重音標量會把 e 轉成 é。
這兩種情況下,字母 é 都代表一個單一的 Swift Character 值,也代表一個可擴充字形群集。第一種情況,字形群集只包含一個標量;第二種情況,則包含兩個標量。
let eAcute: Character = "\u{E9}" // é 代表一個單一 Swift Character 值,也代表一個可擴充字形群集,該群集只含一個標量
let combinedEAcute = "\u{65}\u{301}" // é 代表一個可擴充字形群集,該群集含兩個標量
print("eAcute is \(eAcute) and combinedEAcute is \(combinedEAcute)")
---
output: eAcute is é and combinedEAcute is é可擴充字形群集是一種將許多複雜書寫系統字元表示為單一字元值的彈性方式。例如,來自韓文字母表的韓文音節可以表示為組合或分解的有序排列。在 Swift 中都會被視為同一個單一 Character 值。
let precomposed: Character = "\u{D55C}" // 한
let decomposed: Character = "\u{1112}\u{1161}\u{11AB}" // ᄒ, ᅡ, ᆫ
print("precomposed 的值是 \(precomposed),decomposed 的值是 \(decomposed)")
---
output: precomposed的值是한,decomposed的值是한可擴充字形群集可以讓包圍記號(如 COMBINING ENCLOSING CIRCLE,U+20DD)標量包圍其他 Unicode 標量,作為單一 Character 值。
let enclosedEAcute: Character = "\u{E9}\u{20DD}" // enclosedEAcute 是 é⃝
print(enclosedEAcute)
---
output: é⃝地區指示符號的 Unicode 標量可以組合成單一 Character 值,例如 REGIONAL INDICATOR SYMBOL LETTER H(U+1F1ED) 與 REGIONAL INDICATOR SYMBOL LETTER K(U+1F1F0)。
let regionalIndicatorForHK: Character = "\u{1F1ED}\u{1F1F0}" // HK
print(regionalIndicatorForHK) // regionalIndicatorForHK 是 🇭🇰
---
output: 🇭🇰計算字元數量
若要取得字串中 Character 值的數量,可以用 count 屬性。
let unusualMenagerie = "Koala 🐨, Snail 🐌, Penguin 🐧, Dromedary 🐫"
print("unusualMenagerie has \(unusualMenagerie.count) characters.") // 輸出「unusualMenagerie has 40 characters.」
---
output: unusualMenagerie has 40 characters.注意在 Swift 中,使用可擴充字形群集作為 Character 值來串接或改變字串時,不一定會改變字串的字元數量。
例如,若用四個字元的單字 cafe 初始化新字串,然後加上一個 COMBINING ACUTE ACCENT (U+0301) 作為結尾。最終這個字串的字元數仍然是 4,因為這四個字元現在是 café,長度還是 4。
var word = "cafe"
print("The number of characters in \(word) is \(word.count).") // 輸出「The number of characters in cafe is 4.」
word += "\u{301}"
print("The number of characters in \(word) is \(word.count).") // 輸出「The number of characters in café is 4.」
---
output: The number of characters in cafe is 4.
The number of characters in café is 4.注意
可擴充字形群集可以由多個 Unicode 標量組成。這代表不同字元以及相同字元的不同表示方式可能需要不同數量的記憶體空間來儲存。所以 Swift 中的字元在字串中不一定佔用相同記憶體空間。因此在未取得字串的可擴充字形群集範圍前,無法計算字串的字元數量。如果處理長字串,要注意
count屬性必須遍歷全部 Unicode 標量,才能確定字串的字元數。另外要注意的是,
count屬性回傳的字元數不一定與包含相同字元的NSString的length屬性相同。NSString的length屬性是用UTF-16表示的 16 位元代碼單元數,而不是 Unicode 可擴充字形群集。
存取與修改字串
可以透過字串的屬性與方法來存取與修改它,也可以用下標語法完成。
字串索引
每個 String 值都有一個關聯的索引(index)型別 String.Index,它對應字串中每個 Character 的位置。
前面提到,不同字元可能佔用不同數量的記憶體空間,所以要知道 Character 的確切位置,必須從 String 開頭遍歷每個 Unicode 標量直到結尾。因此,Swift 的字串不能用整數(integer)作為索引。
用 startIndex 屬性可以取得 String 的第一個 Character 的索引。用 endIndex 屬性可以取得最後一個 Character 的後一個位置的索引。因此,endIndex 不能作為有效下標。如果 String 是空字串,startIndex 與 endIndex 相等。
呼叫 String 的 index(before:) 或 index(after:) 方法,可以立即取得前一個或後一個索引,也可以呼叫 index(_:offsetBy:) 方法取得對應偏移量的索引,這種方式可避免多次呼叫 index(before:) 或 index(after:)。
可以用下標語法存取 String 特定索引的 Character。
let greeting = "Jensen Jon!"
print("greeting's first character is \(greeting[greeting.startIndex]).") // J
print("The character before greeting's endIndex is \(greeting[greeting.index(before: greeting.endIndex)])") // !
print("The character after greeting's startIndex is \(greeting[greeting.index(after: greeting.startIndex)])") // e
print("The character with a offset of 7 from greeting's startIndex is \(greeting[greeting.index(greeting.startIndex, offsetBy: 7)])") // J
---
output: greeting's first character is J.
The character before greeting's endIndex is !
The character after greeting's startIndex is e
The character with a offset of 7 from greeting's startIndex is J試圖取得超出範圍的索引會造成執行時錯誤。
//greeting[greeting.endIndex] // 若取消註解,執行時會報錯:Fatal error: String index is out of bounds
//greeting.index(after: greeting.endIndex) // 若取消註解,執行時會報錯:Fatal error: String index is out of bounds用 indices 屬性會建立一個包含全部索引的範圍(Range),用來在字串中存取單一字元。
for index in greeting.indices {
print("\(greeting[index])", terminator: " ") // 輸出「J e n s e n J o n !」
}
print("")
---
output: J e n s e n J o n ! 注意
可以用 startIndex 與 endIndex 屬性,或 index(before:)、index(after:)、index(_:offsetBy:) 方法在任何遵循 Collection 協定的型別中操作。除了 String,也可用於 Array、Dictionary 與 Set。
插入與刪除
呼叫 insert(_:at:) 方法可在字串指定索引插入字元,呼叫 insert(contentsOf:at:) 方法可在指定索引插入一段字串。
var friendlyGreeting = "hello"
friendlyGreeting.insert("!", at: friendlyGreeting.endIndex) // friendlyGreeting 現在等於「hello!」
friendlyGreeting.insert(contentsOf: " there", at: friendlyGreeting.index(before: friendlyGreeting.endIndex)) // friendlyGreeting 現在等於「hello there!」呼叫 remove(at:) 方法可在字串指定索引刪除一個字元,呼叫 removeSubrange(_:) 方法可在指定索引刪除一段子字串。
friendlyGreeting.remove(at: friendlyGreeting.index(before: friendlyGreeting.endIndex)) // friendlyGreeting 現在等於「hello there」
let range = friendlyGreeting.index(friendlyGreeting.endIndex, offsetBy: -6)..<friendlyGreeting.endIndex
friendlyGreeting.removeSubrange(range) // friendlyGreeting 現在等於「hello」
print(friendlyGreeting)
---
output: hello注意
可以用 insert(:at:)、insert(contentsOf:at:)、remove(at:) 與 removeSubrange(:) 方法在任何遵循 RangeReplaceableCollection 協定的型別中操作。除了 String,也可用於 Array、Dictionary 與 Set。
子字串
當開發者從字串中取得子字串,例如用下標或 prefix(_:) 等方法,就會得到一個 Substring 實例,而不是另一個 String。Swift 裡的 Substring 幾乎所有功能都和 String 一樣,代表開發者可以用同樣方式操作 Substring 與 String。不過,和 String 不同的是,只有在短時間內需要操作字串時才會用 Substring。若需長期保存結果,請將 Substring 轉成 String 實例。
let niceGreeting = "Hello, Jensen!"
let index = niceGreeting.firstIndex(of: ",") ?? niceGreeting.endIndex
let beginning = greeting[..<index] // beginning 的值是「Hello」
// 把結果轉成 String 以便長期儲存。
let newString = String(beginning)
print("newString is \(newString).")
---
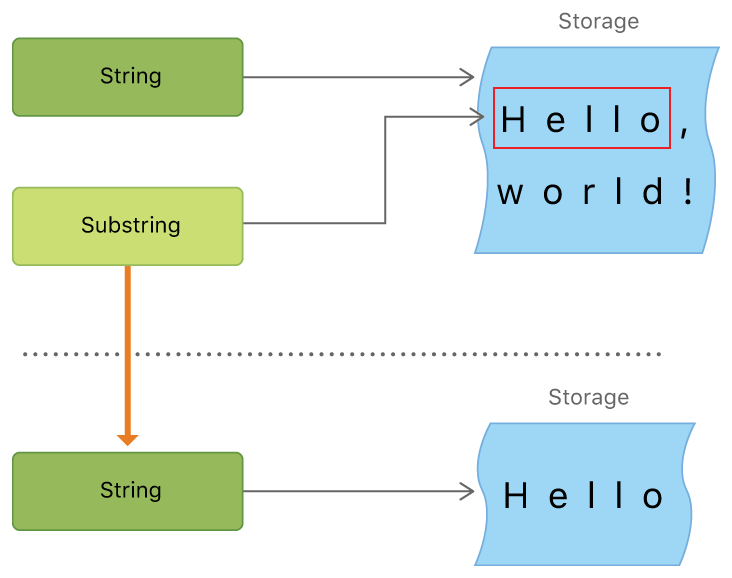
output: newString is Jense.就像 String,每個 Substring 都會在記憶體中保存字元集。而 String 與 Substring 的差異在於效能最佳化,Substring 可以重複利用原本 String 的記憶體空間,或另一個 Substring 的記憶體空間(String 也有同樣最佳化,但如果兩個 String 共用記憶體,它們就會相等)。這個最佳化代表在修改 String 與 Substring 前都不需消耗效能去複製記憶體。正如前述,Substring 不適合長期儲存,因為它重用了原本 String 的記憶體空間,原本的記憶體必須保留直到 Substring 不再被使用。
上述例子中,niceGreeting 是一個 String,代表它在記憶體中有一塊空間保存字元集。而 beginning 是 niceGreeting 的 Substring,它重用了 niceGreeting 的記憶體空間。相對地,newString 是用 Substring 建立的 String,擁有自己的記憶體空間。
注意
String 與 Substring 都遵循 StringProtocol 協定,這代表操作字串的函式若用 StringProtocol 會更方便。可以傳入 String 或 Substring 呼叫函式。
比較字串
Swift 提供三種方式比較文字值:字串字元相等、前綴相等與後綴相等。
字串/字元相等
字串/字元可以用等於運算子 == 與不等於運算子 !=。
let aQuotation = "We're a lot alike, you and I."
let sameQuotation = "We're a lot alike, you and I."
if aQuotation == sameQuotation {
print("These two strings are considered equal.") // 輸出「These two strings are considered equal.」
}
---
output: These two strings are considered equal.如果兩個字串(或兩個字元)的可擴充字形群集標準相等,就認為它們相等。只要可擴充字形群集有相同語意與外觀就認為標準相等,即使它們由不同的 Unicode 標量組成。
例如,LATIN SMALL LETTER E WITH ACUTE (U+00E9) 就標準相等於 LATIN SMALL LETTER E (U+0065) 加上 COMBINING ACUTE ACCENT (U+0301)。這兩個字形群集都是表示字元 é 的有效方式,所以它們被認為標準相等。
let eAcuteQuestion = "Voluez-vous un caf\u{E9}?"
let combinedEAcuteQuestion = "Voluez-vous un caf\u{65}\u{301}?"
if eAcuteQuestion == combinedEAcuteQuestion {
print("These two strings are considered equal.") // 輸出「These two strings are considered equal.」
}
---
output: These two strings are considered equal.相反地,英文的 LATIN CAPITAL LETTER A (U+0041) 不等於俄文的 CYRILLIC CAPITAL LETTER A (U+0410)。兩個字元看起來一樣,但語意不同。
let latinCapitialLetterA: Character = "\u{41}"
let cyrillicCapitalLetterA: Character = "\u{410}"
if latinCapitialLetterA != cyrillicCapitalLetterA {
print("These two characters are not equivalent.") // 輸出「These two characters are not equivalent.」
}
---
output: These two characters are not equivalent.注意
在 Swift 中,字串與字元不區分地區(not locale-sensitive)。
前綴/後綴相等
可呼叫字串的 hasPrefix(_:)/hasSuffix(_:) 方法檢查字串是否有特定前綴/後綴,這兩個方法都接收一個 String 型別參數並回傳布林值。
下例以字串陣列表示莎士比亞劇作《羅密歐與茱麗葉》前兩幕的場景位置。
let romeoAndJuliet = [
"Act 1 Scene 1: Verona, A public place",
"Act 1 Scene 2: Capulet's mansion",
"Act 1 Scene 3: A room in Capulet's mansion",
"Act 1 Scene 4: A street outside Capulet's mansion",
"Act 1 Scene 5: The Great Hall in Capulet's mansion",
"Act 2 Scene 1: Outside Capulet's mansion",
"Act 2 Scene 2: Capulet's orchard",
"Act 2 Scene 3: Outside Friar Lawrence's cell",
"Act 2 Scene 4: A street in Verona",
"Act 2 Scene 5: Capulet's mansion",
"Act 2 Scene 6: Friar Lawrence's cell"
]這時可以呼叫 hasPrefix(_:) 方法計算劇作中第一幕的場景數:
var act1SceneCount = 0
for scene in romeoAndJuliet {
if scene.hasPrefix("Act 1 ") {
act1SceneCount += 1
}
}
print("There are \(act1SceneCount) scenes in Act 1.")
---
output: There are 5 scenes in Act 1.同理,可以用 hasSuffix(_:) 方法計算發生在不同地點的場景數。
var mansionCount = 0
var cellCount = 0
for scene in romeoAndJuliet {
if scene.hasSuffix("Capulet's mansion") {
mansionCount += 1
} else if scene.hasSuffix("Friar Lawrence's cell") {
cellCount += 1
}
}
print("\(mansionCount) mansion scenes; \(cellCount) cell scenes")
---
output: 6 mansion scenes; 2 cell scenes注意
hasPrefix(:) 與 hasSuffix(:) 方法都是在每個字串中逐字元比較其可擴充字形群集是否標準相等。
字串的 Unicode 表示形式
當一個 Unicode 字串被寫入文字檔或其他儲存時,字串中的 Unicode 標量會用 Unicode 定義的幾種編碼格式(encoding forms)編碼。每個字串中的小塊編碼都稱為代碼單元(code units)。這些包括 UTF-8 編碼格式(將字串編碼為 8 位元代碼單元)、UTF-16 編碼格式(16 位元代碼單元),以及 UTF-32 編碼格式(32 位元代碼單元)。
Swift 提供幾種不同方式存取字串的 Unicode 表示形式。可以利用 for-in 遍歷字串,以 Unicode 可擴充字形群集方式存取每個 Character 值。
另外,也能以其他三種 Unicode 相容方式存取字串值:
UTF-8代碼單元集合(用字串的 utf8 屬性存取)UTF-16代碼單元集合(用字串的 utf16 屬性存取)- 21 位元的 Unicode 標量值集合,也就是字串的
UTF-32編碼格式(用字串的 unicodeScalars 屬性存取)
以下由 D、o、g、!!(DOUBLE EXCLAMATION MARK,Unicode 標量 U+203C)與 🐶(DOG FACE,Unicode 標量 U+1F436)組成的字串,每個字元代表不同的表示。
let dogString = "Dog‼🐶"UTF-8 表示
可以遍歷 String 的 utf8 屬性存取其 UTF-8 表示。這是 String.UTF8View 型別的屬性,UTF8View 是無號 8 位元(UInt8)值的集合,每個 UInt8 值都是一個字元的 UTF-8 表示:
| Character | D U+0044 | o U+006F | g U+0067 | ‼ U+203C | 🐶 U+1F436 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTF-8 Code Unit | 68 | 111 | 103 | 226 | 128 | 188 | 240 | 159 | 144 | 182 |
| Position | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
for codeUnit in dogString.utf8 {
print("\(codeUnit) ", terminator: "")
}
print("")
---
output: 68 111 103 226 128 188 240 159 144 182 上例中,前三個十進位 codeUnit 值(68、111、103)代表字元 D、o 與 g,它們的 UTF-8 表示與 ASCII 相同。接下來三個十進位 codeUnit 值(226、128、188)是 DOUBLE EXCLAMATION MARK 的 3 位元組 UTF-8 表示。最後四個 codeUnit 值(240、159、144、182)是 DOG FACE 的 4 位元組 UTF-8 表示。
UTF-16 表示
可以遍歷 String 的 utf16 屬性存取其 UTF-16 表示。這是 String.UTF16View 型別屬性,UTF16View 是無號 16 位元(UInt16)值的集合,每個 UInt16 都是一個字元的 UTF-16 表示:
| Character | D U+0044 | o U+006F | g U+0067 | ‼ U+203C | 🐶 U+1F436 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTF-16 Code Unit | 68 | 111 | 103 | 8252 | 55357 | 56374 |
| Position | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
for codeUnit in dogString.utf16 {
print("\(codeUnit) ", terminator: "")
}
print("")
---
output: 68 111 103 8252 55357 56374同樣,前三個 codeUnit 值(68、111、103)代表字元 D、o 與 g,它們的 UTF-16 代碼單元與 UTF-8 完全相同(因為這些 Unicode 標量表示 ASCII 字元)。
第四個 codeUnit 值(8252)等於十六進位 203C 的十進位值。這代表 DOUBLE EXCLAMATION MARK 字元的 Unicode 標量值 U+203C。這個字元在 UTF-16 中可用一個代碼單元表示。
第五與第六個 codeUnit 值(55357 與 56374)是 DOG FACE 字元的 UTF-16 表示。第一個值為 U+D83D(十進位 55357),第二個值為 U+DC36(十進位 56374)。
Unicode 標量表示
可以遍歷 String 的 unicodeScalars 屬性存取其 Unicode 標量表示。這是 UnicodeScalarView 型別的屬性,UnicodeScalarView 是 UnicodeScalar 型別值的集合。
每個 unicodeScalar 有一個 value 屬性,可回傳對應的 21 位數值,用 UInt32 表示:
| Character | D U+0044 | o U+006F | g U+0067 | ‼ U+203C | 🐶 U+1F436 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode Scalar Code Unit | 68 | 111 | 103 | 8252 | 128054 |
| Position | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
for scalar in dogString.unicodeScalars {
print("\(scalar.value) ", terminator: "")
}
print("")
---
output: 68 111 103 8252 128054 前三個 UnicodeScalar 值(68、111、103)的 value 屬性仍代表字元 D、o 與 g。
第四個 codeUnit 值(8252)仍等於十六進位 203C 的十進位值。這代表 DOUBLE EXCLAMATION MARK 字元的 Unicode 標量 U+203C。
第五個 UnicodeScalar 值的 value 屬性 128054,是十六進位 1F436 的十進位表示。等同於 DOG FACE 的 Unicode 標量 U+1F436。
作為查詢 value 屬性的替代方法,每個 UnicodeScalar 值也可以用來建立新的 String 值,例如在字串插值中使用:
for scalar in dogString.unicodeScalars {
print("\(scalar) ")
}
---
output: D
o
g
‼
🐶